WM Market Reports
Family Offices Gradually Fall More In Love With VC
.jpg)
A report casts its eye over how family offices around the world approach venture capital. Such organizations are often thought of as holders of "patient capital", making them logical partners for VC as an asset class.
Family offices have become more involved in the world’s venture capital deals, latest data in a report shows, increasing their share of the total market and the volume of specific transactions.
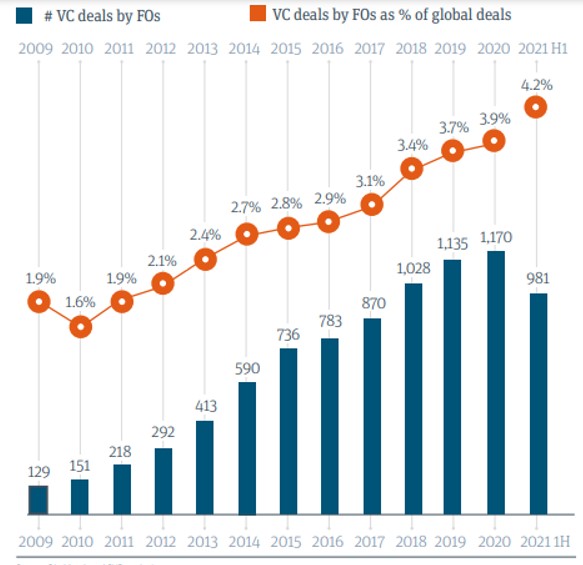
A study of 139 ultra-high net worth families and family offices, as well as follow-on interviews with 10 family offices, found that in the first half of 2021, FO-backed venture deals accounted for 4.2 per cent of the total. That figure was up from 3.9 per cent in 2020 and 2019.
The total number of VC deals by family offices fell to 981 in the first six months of this year; there were 1,179 in the whole of 2020 and 1,235 a year earlier. In 2020, the average family office held eight venture funds and 10 direct venture investments. Today, they hold 10 funds and 17 direct investments. Within the next 24 months, they expect to make 18 new investments (six funds and 12 direct deals).
The findings come from Family Offices Investing in Venture Capital Report, by Silicon Valley Bank and Campden Research.
Such figures underscore how ultra-wealthy families, mindful that they are holders of “patient capital” and with less urgent need for liquidity than some other investors, are a natural fit for the VC sector. Venture capital funds typically have a maturity of around 10 years or more. To justify that relatively low liquidity, they promise superior returns to those in public markets – a compelling proposition at a time of ultra-low interest rates.
Among the main takeaways from the report are that investments tend to be focused on growth areas, at 48 per cent of the venture portfolio, followed by 28 per cent in pre-seed and seed investments and 24 per cent in Series A investments. Meanwhile, the study found that family office staff and VC teams are growing, but top talent is in short supply. Today the average family office staff consists of 15 members, including two VC investment professionals, with plans to bring in one additional venture capital specialist within the next five years.
Some two-thirds (67 per cent) of family offices rely on their existing network for deal flow, as the best venture deals continue to be hard to access. Most family offices rely on their existing networks, GPs of venture funds, founders, and other family offices for deal flow. Only 1 per cent currently use digital platforms.
Perhaps understandably in the age of COVID-19, the report found that 18 per cent of family offices have venture investments in life sciences, e.g., biopharma, drug discovery, medical devices, diagnostics, etc. Energy and resource innovation, including climate and sustainability, is an increasing area of focus. Notably, a family office was behind the team in Germany developing the BioNTech vaccine for Pfizer, as revealed by Highworth Research. (This news service is exclusive media partner with Highworth, which is a database and research facility for single family offices.)
The family offices have headquarters across 30 countries, with 49 per cent cent being in North America, 27 per cent in Europe, and 25 per cent in the rest of the world.
Other numbers
Globally, the average single-family office with experience in
venture capital manages $989 million in assets – or 75 per cent
of the average $1.3 billion in family net wealth (compared with
$797 million in AuM reported in our 2020 report). However, 66 per
cent of the offices manage up to $500 million. The report noted
that family offices “tend to follow a similar path in their
venture capital journeys.”
Family offices often begin with fund of funds - a convenient option, which can provide diversified exposure, including to established managers - and ad hoc direct investments referred from friends and family - which help them gain crucial experience, the report said.
Single-family offices employ a variety of structures for their venture investments, including an annual allocation (29 per cent of the relevant participants), a special purpose vehicle to capitalize on opportunities as they arise (28 per cent), and a venture fund with management team and single limited partner (i.e., the family) (21 per cent). Funds with a single LP are relatively more popular in North America (31 per cent versus 11 per cent for the rest of the world). SPVs and subsidiaries with a dedicated pool of capital are relatively more popular in the rest of the world (32 per cent and 18 per cent, respectively - versus 24 per cent and 7 per cent, respectively, for North America).
As of August 31, 2021, $418 billion was invested in venture capital deals globally, surpassing the full year record established in 2020 of $333 billion.